

#547 transistor series#
A resistor is always added in series with the base pin since a transistor will be destroyed by currents greater than 5 mA.
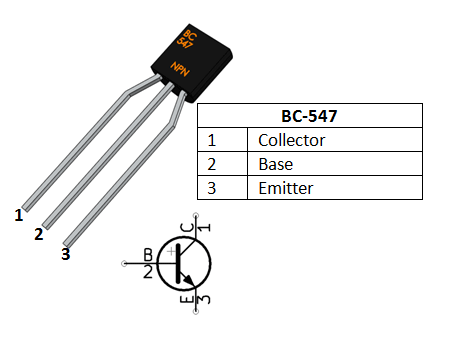
The maximum biassing current should be 5mA, as was previously stated. This biassing is accomplished by applying the necessary current to the base pin. A transistor will operate as an Open switch during forwarding Bias and as a Closed switch during Reverse Bias. WHEN THE TRANSISTOR ACTS AS A SWITCH:Īs previously mentioned, a transistor is operated in the Saturation and Cut-Off Region then it acts as a switch.

However, this only happens when a very small biassing current, designated Ib, passes through the transistor's base terminal. When the transistor is turned ON, the IC supplies a significant amount of current between its collector and emitter terminals. Because the control that the base exercises over the collector to emitter current results in the transistor's amplifying capabilities. The connection between the input and output circuits is the primary property of this transistor action. The transistor action of an NPN bipolar transistor is represented by the flow of electrons using the base. The highest base current is constrained by this resistor's restriction of current flow. Through the RL, the collector terminal is connected to the VCC. The transistor's base terminal is always positive to the emitter, and the collector voltage supply is always positive concerning the emitter terminal.

The transistor has a +Ve voltage at its base and a -Ve voltage at its emitter. To bias a transistor, current must be supplied to the base pin this current (IB) should be kept to a maximum of 5mA. We cannot use this transistor to connect loads that use more than 100mA since the maximum amount of current that can pass via the Collector pin is 100mA. The gain value of the BC547 transistor, which ranges from 110 to 800, affects the transistor's capacity for amplification. An NPN transistor's base is shown by a short vertical line, and the emitter, is shown by a diagonal line connecting the base and it is represented by an arrowhead pointing away from the base. This transistor's primary tasks are switching and amplification. This transistor's base terminal, which has a little current, controls the emitter and base terminals' higher current. An amplifier of current, a transistor is nothing more than the transfer of resistance. Specifically, it is a BC547 NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
